
Security researchers, found a critical account takeover vulnerability in the OpenAI ChatGPT application that allowed an attacker to take over someone’s account, access their chat history, and view their billing information without their knowledge.
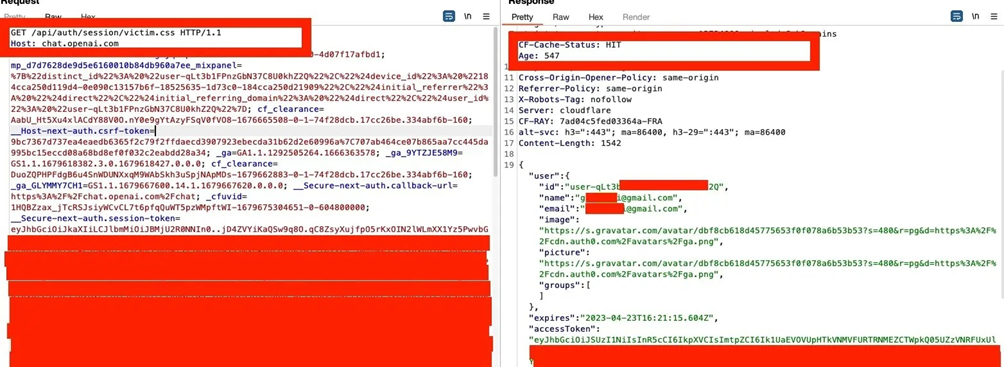
The issue was reported by a security researcher who explored the authentication flow in ChatGPT’s requests and discovered an anomaly in the GET request. The request fetched the account context, including email, name, image, and access Token from the server, allowing the researcher to exploit “Web Cache Deception.”
EndPoints
https://chat.openai.com/api/auth/session
https://chat.openai.com/api/auth/session/test.css
The researchers explained that to exploit the vulnerability, they had to force the Load Balancer to cache the request on a specific path, and if successful, they could read the victim’s sensitive data from the cached response.
Web cache deception
“Web cache deception” is a vulnerability that allows an attacker to manipulate web cache servers to store sensitive information in a cached response. By crafting a specific request with a modified file extension, an attacker can trick the cache server into storing sensitive data, which can then be accessed later.
The vulnerability works because many web cache servers are configured to cache responses based on the file extension of the requested resource. For example, a cache server might cache all resources with the “.css” file extension to improve performance. However, if an attacker can trick the server into caching a response that contains sensitive information, they can then retrieve that information later by accessing the cached response.
OpenAI’s response to this vulnerability was to manually instruct the caching server not to cache the endpoint through a regex.
This vulnerability has since been fixed, and OpenAI’s team praised the researchers for their responsible disclosure.
